Quenching is a rapid heat treatment process to transform martensite (or bainite) transformation below Ms temperature or near Ms. The detailed method is to heat the steel to a temperature above the critical temperature of Ac3 (hypoeutectoid steel) or Ac1 (hyper-eutectoid steel), then retain its heat for a period of time, make it all or part austenitized, and finally cool it at a critical cooling rate. The solution treatment of materials such as aluminum alloys, copper alloys, titanium alloys, tempered glass, or heat treatment processes with rapid cooling processes is also referred to as quenching. Quenching is a generic heat treatment process used primarily to increase the hardness of materials. Usually by categories of quenching mediums, it can be divided into water quenching, oil quenching, organic quenching and the like. With the development of science and technology, some new quenching processes have emerged.
1.High pressure gas quenching(HPGQ)
The workpiece is rapidly and evenly cooled in a strong inert gas flow, which can prevent surface oxidation, avoid cracking, reduce distortion, and ensure the required hardness. HPGQ is mainly used for quenching of tool steel, which has recently progressed rapidly. At present, there are negative pressure (<1×105 Pa) high-flow rate air-cooling, pressure (1×105~4×105 Pa) air-cooling and high pressure (5×105~ 10×105 Pa) Air-cooled, ultra-high pressure one (10×105~20×105 Pa) air-cooling and other new technologies that greatly improve not only the vacuum gas quenching ability, but also the status of the quenched workpiece, which are with good surface brightness and small deformation. HPGQ’s mainly used for quenching and tempering of materials, solid solution of stainless steel&special alloys. When quenching with 6×105 Pa high-pressure nitrogen, the high-speed steel (W6Mo5Cr4V2)’s hardenability can be hardened to 70-100 mm, and the high-alloy steel’s can reach 25-100 mm. Cold work die steel (such as Cr12) can reach 80~100 mm.
When quenching with 10 x 105 Pa high-pressure nitrogen gas, the load density is increased by about 30% to 40% when cooled by a cooling load of 6 × 105 Pa. When quenching with 20×105 Pa ultra-high pressure nitrogen or a mixture of helium and nitrogen, the density of the cooled load is 80%-150% higher than that of 6×105 Pa nitrogen cooling, which can cool all high-speed steel and high-alloy steel. , hot work die steel Cr13% chrome steel, and more alloy oil quenched steel, such as larger size 9Mn2V steel. Besides, A dual chamber air-cooled quench furnace with a separate cooling chamber has a better cooling capacity than a single chamber furnace of the same type. The cooling effect of a 2 x 105 Pa nitrogen cooled dual chamber furnace is comparable to a 4 x 105 Pa single chamber furnace. Single-chamber furnaces have lower operating and maintenance costs.
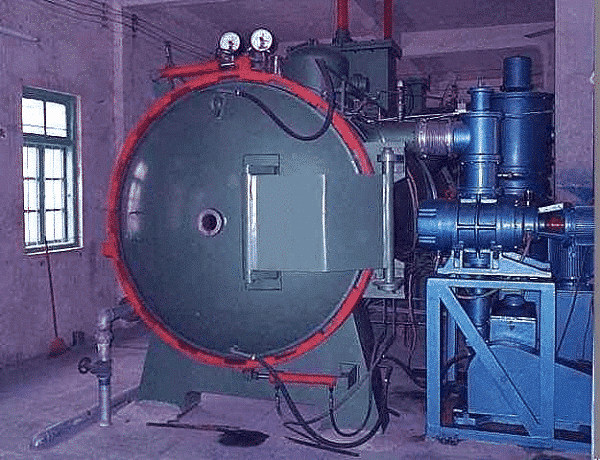
Figure 1 High pressure gas cooled vacuum furnace
2.Intense quenching
Conventional quenching is usually carried out with oil, water or a polymer solution, while intense quenching is carried out with water or a low concentration of brine. The strong quenching feature is that the cooling rate is extremely fast without worrying about excessive distortion and cracking of the steel.
When the conventional quenching is cooled to the quenching agent temperature, the surface of the steel part forms a tensile stress or a low stress state, while the intense quenching stops the cooling while the core of the workpiece is still in a hot state, and the surface layer forms a compressive stress. Under intense quenching conditions, when the cooling rate of the martensite transformation zone is >30 °C / s, the supercooled austenite of the surface of the steel is subjected to a compressive stress of 1200 MPa, which increases the yield strength of the steel after quenching by at least 25%.
The principle of intense quenching: When steel is quenched from austenitizing temperature, the temperature difference between the surface and the core will cause internal stress. The specific volume change and phase change plasticity of the phase change structure also cause additional phase transformation stress. If the thermal stress and the phase transition stress are superimposed, that is, the composite stress exceeds the yield strength of the material, plastic deformation occurs; if the combined stress exceeds the tensile strength of the hot steel, a quench crack is formed. During the intense quenching process, the residual stress caused by the phase transformation plasticity and the specific volume change caused by the specific volume change of the austenite-martensite transformation increase. During intense cooling, the surface of the workpiece is immediately cooled to the bath temperature, and there is almost no change in the core temperature. Rapid cooling causes high tensile stresses due to surface layer shrinkage and stress balance by the core. The increase of the temperature gradient increases the tensile stress caused by the initial martensite transformation, and the increase of the martensite transformation initiation temperature Ms causes the surface layer expansion caused by the phase transformation plasticity, and the surface tensile stress is significantly reduced and converted into compressive stress. The surface compressive stress value is proportional to the amount of surface martensite formed. This surface compressive stress determines whether the core will undergo a martensitic transformation under compression or reverse the surface tensile stress upon further cooling. If the martensite transformation causes the core volume to expand sufficiently, and the surface martensite is very hard and brittle, the surface layer will be broken due to stress reversal. For this reason, the compressive stress on the surface of the steel and the martensite transformation of the core should occur as late as possible.
Strong quenching test and properties after steel quenching: The advantage of the strong quenching method is that compressive stress is formed on the surface layer, the probability of cracking is reduced, and the hardness and strength are improved. The surface layer forms a 100% martensite structure, which will give the largest hardened layer for a given steel grade. Therefore, carbon steel can be used instead of the more expensive alloy steel. Strong quenching can also promote uniform mechanical properties and minimize workpiece distortion. After intense quenching of the part, the service life under alternating load can be increased by an order of magnitude. [1]
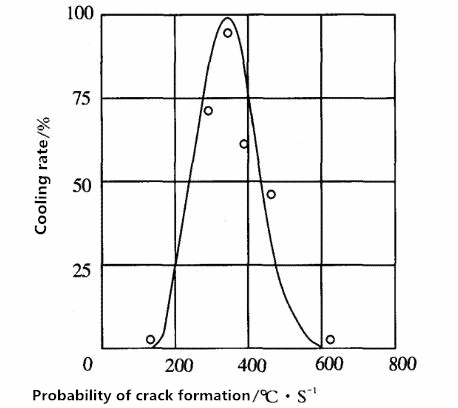
Figure 2 Relationship between the probability of intense quenching crack formation and cooling rate
3. water air mixture cooling method
By adjusting the pressure of the water and air and the distance between the atomizing nozzle and the surface of the workpiece, the cooling capacity of the water-air mixture can be varied and the cooling can be made uniform. The production practice shows that the surface induction heating quenching of complex carbon steel or alloy steel parts can effectively prevent the occurrence of quenching cracks.

Fig. 3 Water-air mixture
4. boiling water quenching method
Cooling with boiling water at 100 ° C, a better hardening effect can be obtained for quenching or normalizing steel. This technology has been successfully applied to the quenching of ductile iron. Taking aluminum alloy as an example: According to the current heat treatment specifications for aluminum alloy forgings and die forgings, the quenching water temperature is generally controlled below 60 ° C. The quenching water temperature is low, the cooling rate is fast, and a large residual stress is generated after quenching. When the product is finally machined, due to the inconsistent surface shape and size, the internal stress is out of balance, resulting in the release of residual stress, causing distortion, bending, ellipse and other deformations of the machined parts, becoming an irreparable final waste, with serious losses. . For example: Aluminum alloy forgings such as propellers and compressor blade discs are obviously deformed after machining, resulting in oversized parts. When the quenching water temperature is raised from room temperature (30-40 ° C) to boiling water (90-100 ° C), the residual stress of the forging is reduced by about 50% on average. [2]
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of boiling water quenching
5. hot oil quenching method
The hot quenching oil is used to make the temperature of the workpiece before or after further cooling equal to or close to the temperature of the Ms point, so as to minimize the temperature difference, and effectively prevent the distortion and cracking of the quenched workpiece. Quenching a small-sized alloy tool steel refrigeration die in hot oil at 160-200 °C can effectively reduce distortion and avoid cracking.

Figure 5 Schematic diagram of hot oil quenching
[1]Fan Dongli. Strong quenching——a new heat treatment method for reinforced steel[J]. Heat Treatment, 2005, 20(4): 1-3
[2] Song Wei, Hao Dongmei, Wang Chengjiang. Effect of boiling water quenching on microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy forgings[J]. Aluminium Machining, 2002, 25