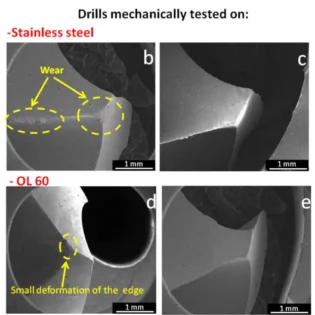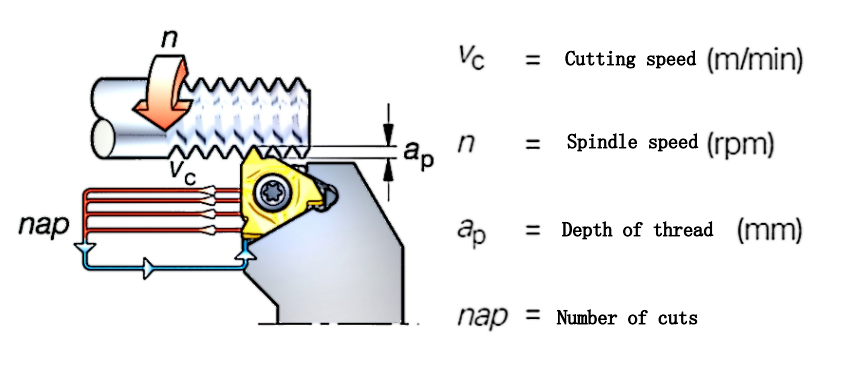
I. Key Fundamental Knowledge on Thread Machining
Terminology Definitions


① Root② Flank③ Crest

What is the Helix Angle?
- The helix angle depends on the diameter and pitch of the thread.
- Adjust the flank clearance angle of the insert by changing the shim.
- The rake angle is denoted as γ. The most common rake angle is 1°, corresponding to the standard shim in the tool holder.
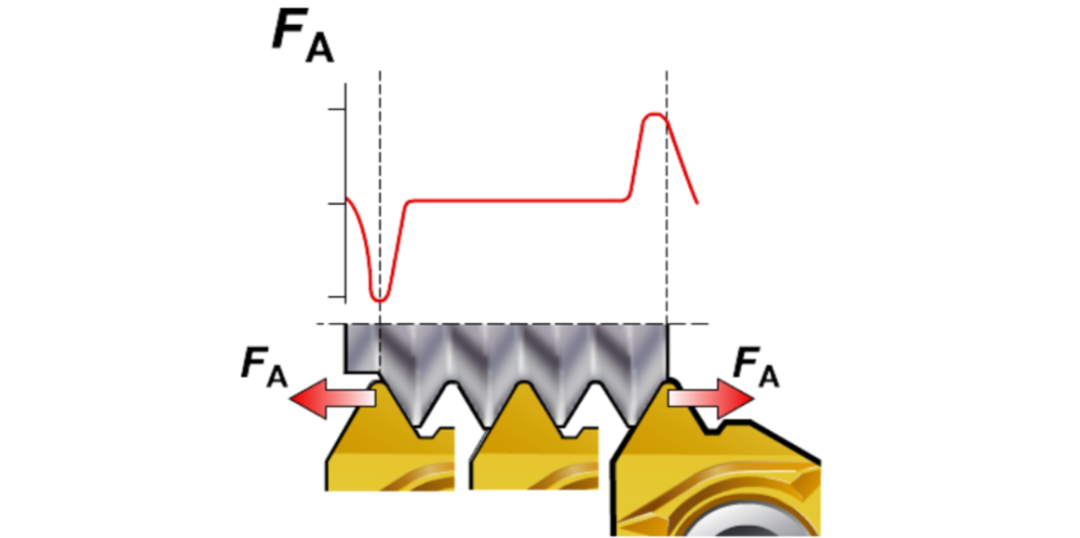
Cutting Forces During Thread Insertion and Exit
- The highest axial cutting force in the thread machining process occurs during the tool’s entry and exit from the workpiece.
- Excessive cutting parameters may cause the insert to move if it is not securely clamped.
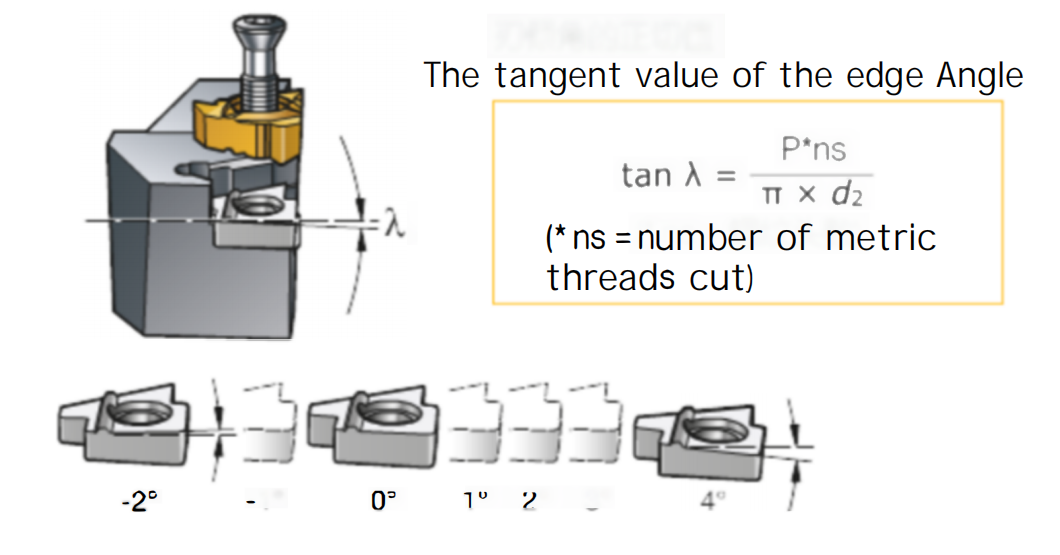
Function of the Rake Angle
The rake angle can be set by using a shim underneath the insert in the tool holder. You can refer to the charts in the tool catalog to choose which shim to use. All tool holders come equipped with a standard shim that sets the rake angle to 1°.
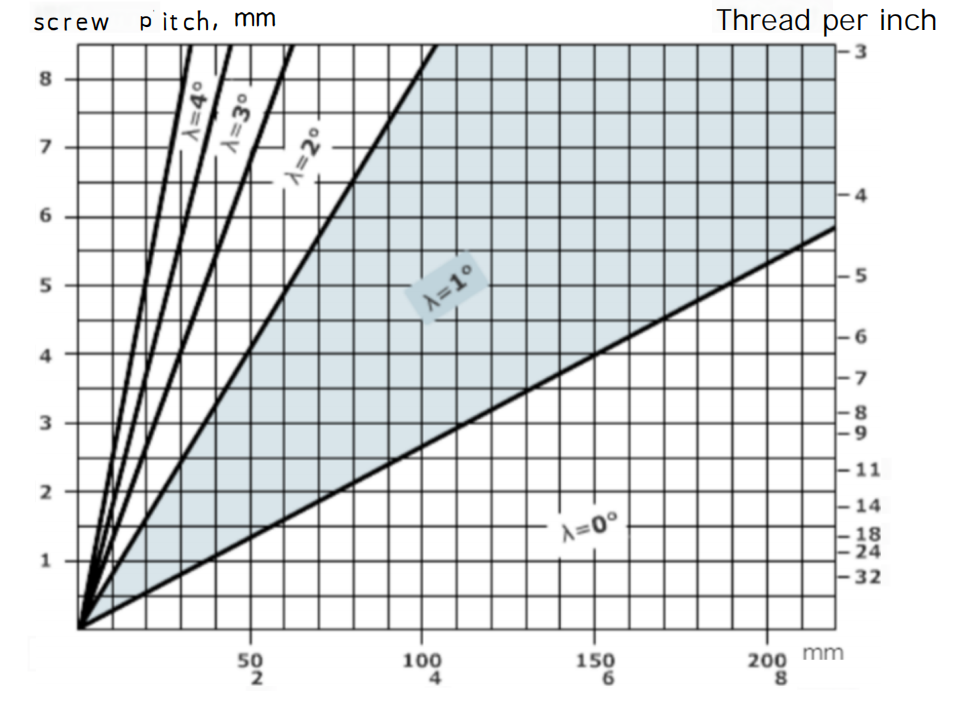
Selecting Shims Based on the Rake Angle
The rake angle is influenced by the workpiece diameter and thread pitch. As shown in the diagram below, for a workpiece with a diameter of 40mm and a pitch of 6mm, the required shim must have a 3° rake angle (the standard shim cannot be used).
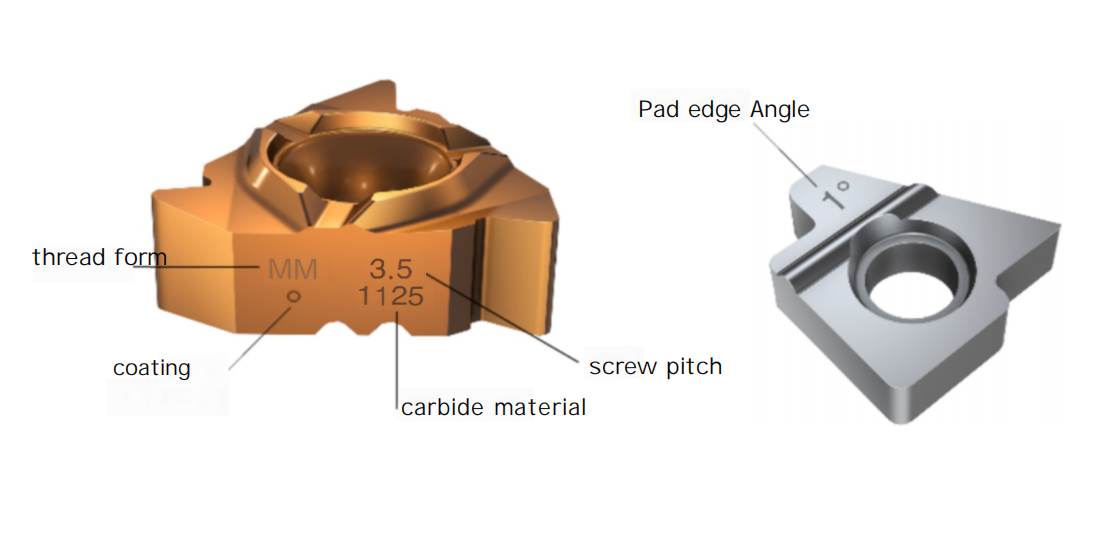 Marking of Threading Inserts and Shims
Marking of Threading Inserts and Shims
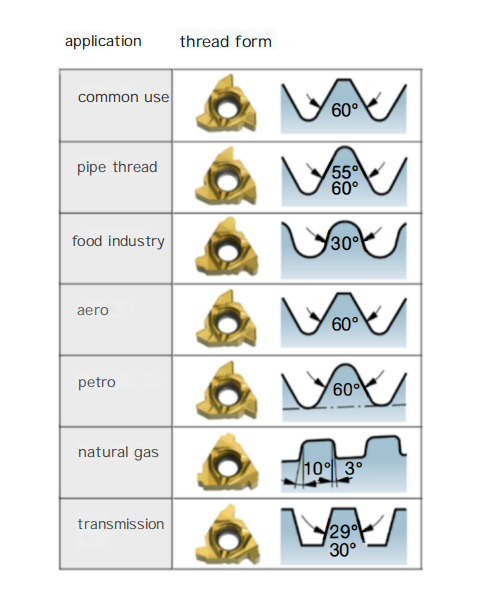
Thread Forms and Their Applications
II. Types of Threading Inserts and Clamping Solutions
Multi-Tooth Inserts
Advantages:
- Reduces the number of tooling passes.
- Extremely high productivity.
Nh??c ?i?m:
- Requires stable clamping.
- Requires sufficient tool retraction space after thread machining.
Full-tooth cutter

Advantages:
- Better control of thread shape.
- Fewer burrs.
Nh??c ?i?m:
- Each blade can only cut one pitch.
V-tooth cutter.

Advantages:
- Flexibility, as the same type of blade can be used for machining several pitches. Disadvantages:
- May result in burr formation, requiring deburring.
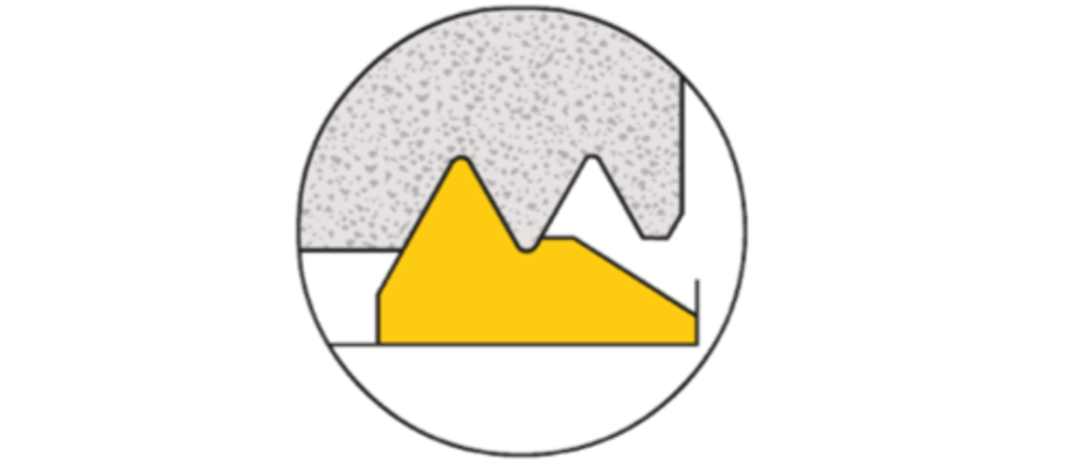
Ⅲ.three different types of feed methods
The feed method plays an important role in the thread machining process. It affects cutting control, blade wear, thread quality, and tool life.
Improved lateral feed
This feed method is commonly used in most CNC machine tools through a looping program.
- Chips are easier to form and guide compared to traditional turning types;
- Axial cutting forces reduce the risk of vibration;
- The chips are thicker but only contact one side of the blade;
- Heat transfer to the blade is reduced;
- Preferred for most thread machining processes.
Radial feed
This is the most commonly used method and also one of the earliest methods that non-CNC lathes could employ.
- Produces hard “V”-shaped chips.
- Uniform blade wear.
- Blade holder exposed to high temperatures, limiting the depth of cut.
- Suitable for machining fine-pitch threads.
- May result in vibration and poor chip control when machining coarse-pitch threads.
- Preferred for machining hardened materials.
Alternating feed of thread machining
- Recommended for large pitches.
- Enables uniform blade wear and maximizes tool life when machining threads with extremely large pitches.
- Chips are guided in two directions, making control difficult.
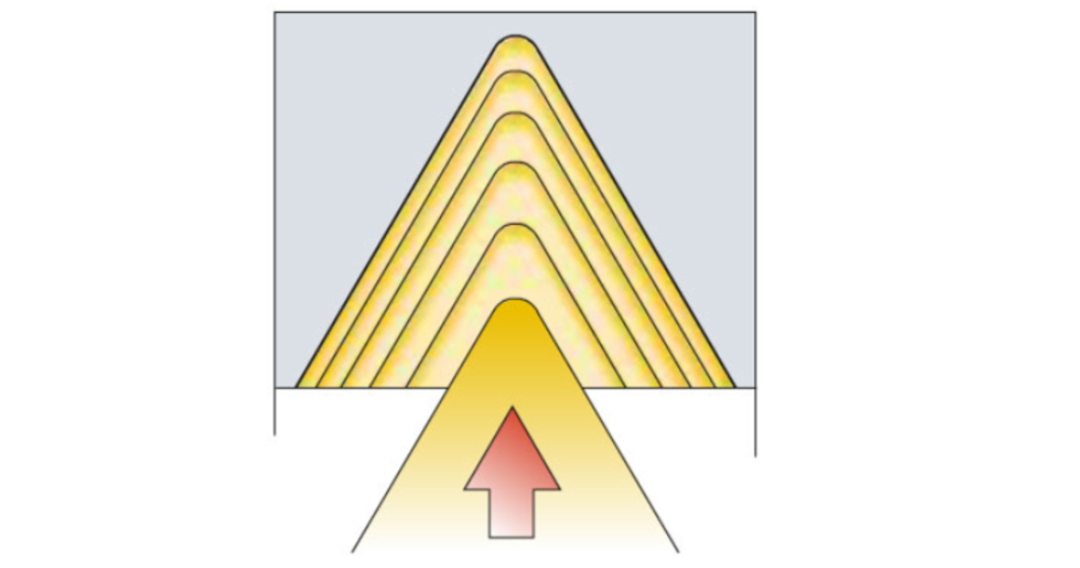
Ⅳ.Methods for Improving Machining Results
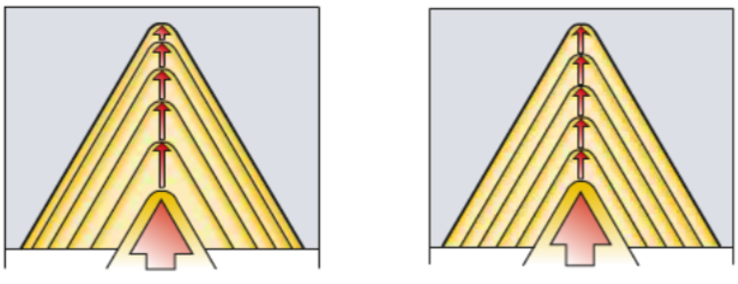
Left: Step-down cutting depth (Constant chip area) Achieves a constant chip area, which is the most common method used in CNC programs.
- The first pass cuts the deepest.
- Follow the recommended values ??on the feed table in the sample.
- Balances chip area more evenly.
- The final pass actually measures around 0.07mm.
Right: Constant cutting depth Regardless of the number of passes, the depth of cut remains the same each time.
- Requires higher demands on the blade.
- Ensures optimal chip control.
- Not applicable for pitches greater than TP1.5mm or 16TP.
Utilizing additional allowance for thread crest finishing: Before machining threads, there’s no need to turn the blank to an exact diameter; utilize additional allowances/material for finishing the thread crest. For finishing crest inserts, leave 0.03~0.07mm of material from the preceding turning process to shape the crest correctly.