Basic Definitions of Positive and Negative Rake Angle Tools
Positive Rake Angle Tool
A positive rake angle tool refers to a turning tool where the front face is inclined toward the interior of the workpiece relative to the cutting point, resulting in a positive rake angle (typically +5° to +15°). Its structural characteristic is a relatively sharp cutting edge, with a smaller contact area between the front face and the chip.
Negative Rake Angle Tool
A negative rake angle tool, on the other hand, has a front face inclined outward from the workpiece relative to the cutting point, resulting in a negative rake angle (typically -5° to -10°). Its structural feature is a blunter cutting edge, with a thicker and more robust tooltip.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Positive and Negative Rake Tools
Positive Rake Angle Tool
Advantages:
Lower Cutting Forces: A positive rake angle allows smoother chip flow and reduces deformation, decreasing main cutting forces by 15–25%.
Better Chip Evacuation: Shorter chip-tool contact length reduces built-up edge formation.
Suitable for Finishing: Minimizes vibration, enabling better surface finish (Ra < 1.6 μm).
Dezavantajlar?:
Lower Tooltip Strength: The positive geometry reduces material support, making the tool prone to chipping in interrupted cuts or hard materials.
Poor Heat Dissipation: Smaller chip-tool contact area limits heat transfer, accelerating crater wear at high speeds.
Shorter Tool Life: Typically 60–70% of negative rake tools under the same conditions.
Negative Rake Angle Tool
Advantages:
High Tooltip Strength: The negative angle creates a “support wedge,” improving impact resistance by >50%.
Superior Heat Dissipation: Larger chip-tool contact area enhances heat conduction, reducing cutting temperatures by 15–30°C.
Multi-Sided Usability: Often designed with double-negative angles, allowing flipping for extended use.
Limitations:
Higher Cutting Forces: Negative rake increases chip deformation, raising main cutting forces by 20–30%.
Greater Power Demand: Requires 15–20% more motor power from the machine tool.
Vibration Risk: Prone to chatter in long overhang machining due to increased cutting forces.
Experimental Comparison
The following systematic experiment compares the performance of carbide positive and negative rake tools under different machining conditions, providing practical insights for tool selection.
Experimental Design
1.Materials & Equipment:
Positive rake tool (+8° rake angle)
Negative rake tool (-6° rake angle)
Both use YG8 karbit substrate with TiAlN coating and 0.4 mm nose radius.
2.Workpiece:45# steel (Φ50×200 mm), quenched and tempered to HRC 28–32.
3.Machine:CA6140 lathe with 3-jaw chuck and tailstock center.
4.Measurement Instruments:
Surface roughness tester (Mitutoyo SJ-210)
Electron microscope (OLYMPUS DSX510)
Cutting force dynamometer (Kistler 9257B)
Infrared thermometer (Fluke Ti400)
5.Parameters
Fixed: Depth of cut (ap = 1 mm), feed rate (f = 0.15 mm/rev).
Variable: Cutting speed (v = 60–180 m/min).
Three repetitions per condition for reliability.
Results & Analysis
Tool Wear & Life Comparison
Using flank wear VB = 0.3 mm as the failure criterion:
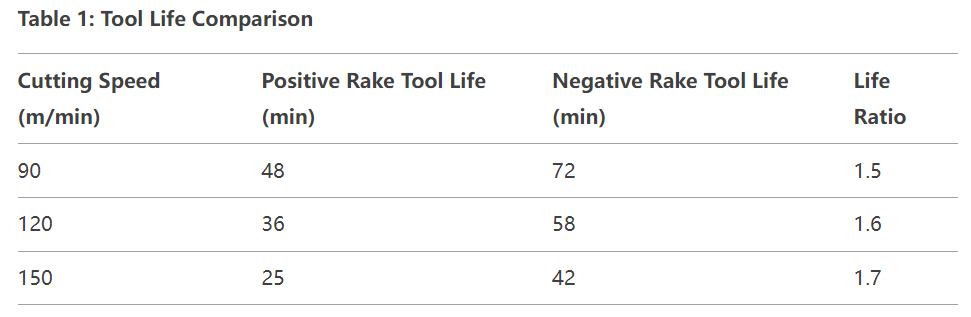
Negative rake angle tools demonstrate significantly longer service life, exceeding positive rake tools by an average of 50-70%. Analysis of wear patterns reveals that positive rake tools primarily fail through crater wear on the rake face and tooltip chipping, whereas negative rake tools exhibit more uniform flank wear, demonstrating superior fracture resistance.
Cutting Force Comparison
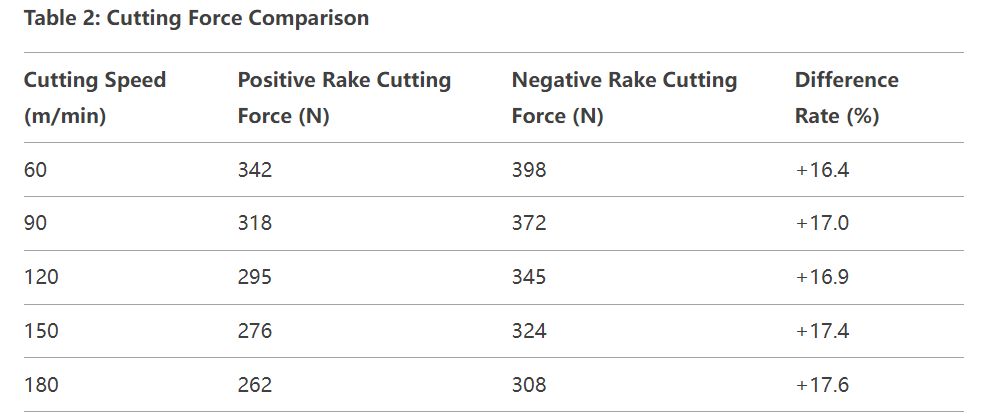
The data shows that under all tested cutting speeds, negative rake tools generate significantly higher principal cutting forces than positive rake tools, with an average increase of approximately 17%. This is attributed to the negative rake design’s larger contact area between the tool’s rake face and chips, as well as intensified cutting deformation. Notably, while cutting forces for both tool types decrease with increasing cutting speed, the difference ratio remains essentially stable.
Cutting Temperature Comparison
Results indicate that negative rake tools maintain consistently lower cutting temperatures than positive rake tools, typically by 15-25°C. This thermal advantage primarily stems from the negative rake design’s enhanced tooltip strength and improved heat dissipation capacity. The temperature difference becomes particularly pronounced during high-speed cutting (v>120m/min), reaching approximately 30°C.
Surface Quality Evaluation
Surface roughness serves as a critical indicator of machining quality. At a feed rate of f=0.15mm/rev, measurements show:
Positive rake tool surface roughness (Ra): 1.6-2.0μm
Negative rake tool surface roughness (Ra): 1.2-1.5μm
Electron microscope observations reveal that surfaces machined with negative rake tools exhibit more uniform texture patterns with fewer burrs and vibration marks. This improvement results from the negative rake design’s enhanced system rigidity that reduces cutting vibrations. Furthermore, negative rake tools maintain more stable tooltip geometry during machining, avoiding the surface quality degradation caused by micro-chipping that often occurs with positive rake tools.
Conclusions
1.While carbide negative rake tools show slightly inferior performance in cutting force, they demonstrate clear advantages in cutting temperature control, surface quality, and tool life.
2.The performance advantages of negative rake tools become more pronounced at higher cutting speeds, making them particularly suitable for modern high-speed machining requirements.
3.Positive rake tools excel in reducing cutting forces and are better suited for machining systems with limited rigidity.
4.Optimal tool angle selection should comprehensively consider multiple factors including workpiece material, machine tool conditions, and specific machining stages.