With the rapid development of China’s automotive industry, especially in the booming new energy vehicle sector, lightweighting has become a core topic. The key to lightweighting is changing traditional materials. Aluminum alloys, with their high strength and low weight, are essential for achieving vehicle lightweighting. The complex geometric shapes of automotive parts and the increasing proportion of die-cast aluminum alloy parts in vehicles have led to a growing demand for CNC machining of die-cast parts.
CNC machining of aluminum alloy automotive parts requires high efficiency, stable continuous production, and decreasing costs, necessitating more detailed control and planning of the entire production process.

Tool Build-Up
Aluminum’s inherent property of low melting point causes it to become “sticky” during cutting. Due to this characteristic and inadequate cooling in actual conditions, the heat generated by friction during the microscopic cutting process cannot be released in time or effectively. This results in aluminum melting and adhering to the tool’s cutting edges and chip flutes. Upon cooling, the aluminum solidifies and sticks to the tool, forming build-up. This phenomenon, commonly referred to in the industry as “easy tool sticking,” leads to tool failure.
Tools are consumables in CNC machining processes and represent a significant cost component. Generally, cutting tools for aluminum alloys need to be sharper, with chip flutes specially polished and coated with aluminum-specific coatings to improve chip removal efficiency. The automotive industry’s push for high efficiency increases feed rates and cutting speeds, which raises the heat generated during cutting and the risk of aluminum melting and sticking to the tool, thereby increasing costs due to tool failure from build-up.
With environmental regulations, minimal quantity lubrication (MQL) is widely used as a cutting fluid alternative in aluminum alloy CNC machining. However, the low melting point of aluminum exacerbates the reduced cooling effect of MQL, further promoting build-up. Tools that fail due to sticking account for about 40% of conventional tool failures. Traditional methods of dealing with build-up, such as tapping or striking, rarely restore tools for reuse. Thus, a new solution is proposed.
Treatment Measures
The new solution involves the following steps:
- Remove the tool with build-up.
- Obtain solid NaOH, dilute it with water, and place it in a ceramic container.
- Once diluted into NaOH solution, immerse the tool with aluminum build-up in the solution. Ensure that the build-up areas are fully submerged and maintain immersion for 2 hours, or adjust based on practical conditions. Table 1 compares traditional and new treatment methods.
| Traditional Treatment | New Solution |
|---|---|
| Tools with aluminum build-up are discarded directly, leading to significant production costs | Immersion liquid can remove aluminum from complex and irregular shapes |
| Physical methods like tapping and striking damage the polished surface, leading to tool discard or reduced cutting efficiency | Short treatment time and simple operation |
| Short treatment time and simple operation | Easy-to-obtain treatment materials with low cost |
Chemical Principles
Using A1Si7Mg material commonly found in automotive parts as an example, where A1 content is approximately 93.5%, Si content is 6.5%, and Mg content is 0.25%. Both Al and Si react with NaOH solution. Immersion in NaOH solution removes the primary A1 component from the tool. The principle involves the reaction between metal and NaOH, producing bubbles (H?), which eventually causes the adhered aluminum to detach.
Chemical reaction equations are as follows:
- Si reacts with NaOH: Si + 2NaOH + H?O → Na?SiO? + 2H?↑
- Al reacts with NaOH: 2Al + 2NaOH + 2H?O → 2NaAlO? + 3H?↑
The final result is the removal of aluminum, making the tool reusable.
Experimental Validation for Reducing Build-up
The theoretical method was tested using a tap. Taps are valuable tools in aluminum alloy machining, requiring a longer lifespan and featuring complex geometric shapes. Once aluminum adhesion occurs, physical removal is nearly impossible, making this test more significant and representative.
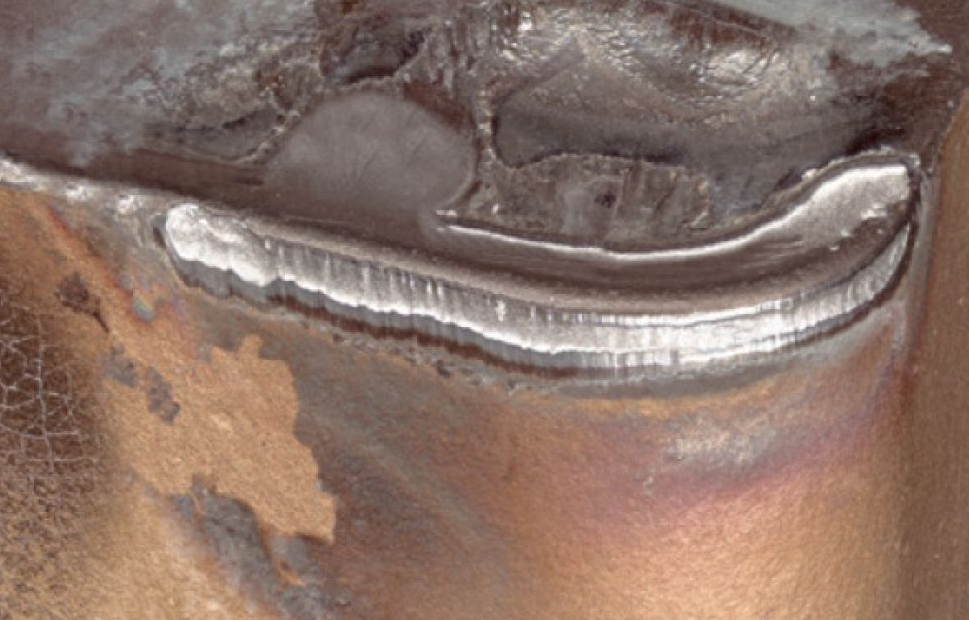
Due to high heat generated during machining and possible inadequate cooling, aluminum melts instantly and adheres to the flutes rendering the tap unusable due to damaged threads.
The test involved immersing the tap with aluminum build-up in NaOH solution.
The test conclusion: The tap, after complete immersion in NaOH, showed that the build-up had completely detached. Residual aluminum slag was found in the test container. The treated tap was used for further machining, and the workpiece threads met the required specifications. The tap was successfully restored for reuse.

??züm
The automotive parts industry, characterized by mass production, requires extensive cutting validation during the initial equipment and tool design phase. Common issues such as build-up during validation due to parameter mismatches, equipment adjustments, and operator experience can significantly increase trial costs and production cycles. This method effectively addresses build-up issues, greatly reducing tool costs and processing time, extending tool life, and substantially lowering production costs.