What Should You Know about Parting Tools and Parting Operation
La troncatura consiste nell'inserire uno strumento simile a una lama direttamente nel pezzo in lavorazione e tagliare il pezzo in lavorazione con una certa lunghezza. Di solito viene utilizzato per rimuovere l'estremità finita del pezzo dalla barra nel mandrino. Altri usi includono il taglio della testa del bullone.
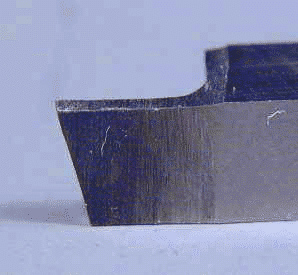
Commercial parting tool
There are many kinds of commercial parting tools provided by tool suppliers, but most of them are too large to be used on 7×10.

This is problematic because the top of the parting tool must be centered. The 7×10 interest group described many attempts (including my own), including grinding, turning, and grinding, to remove 1 / 16 “from the bottom of the carriage, but with little success. The tool holder is quite hard metal.
Even so, the gadget is tempting, because grinding a separation tool from a tool blank is painful – because so much metal has to be ground off – and the separation tool becomes dull and brittle. This tool and similar large tools use preformed tools. If you break the end, you just need to grind a new tip and continue. I haven’t done that yet, but the best solution is to use the high frequency 5 / 16 “parting tool, which may just make a custom tool holder of the right height.
This is another 1 / 2 “business separation tool. I plan to customize a knife rest for it one day.

Tailor ground separation tool
Grinding your own separation tool is not really difficult, but it takes a long time and produces a lot of metal and grinding dust, because relatively large amounts of metal you have to move from blank. Here are some typical pictures of household ground tools. Note that the tool is tapering from top to bottom (like a narrow trapezoid), tapering from front to back, providing safety for the cutting head. The top of the tool has been ground down by several thousandths of an inch to align the top edge of the tool with the lathe centerline. If you have a tool holder with an adjustable tool height, you do not have to. Forming a parting blade near the edge of the tool allows the tool to work near the chuck jaws.
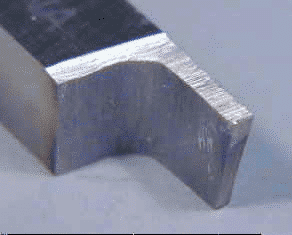
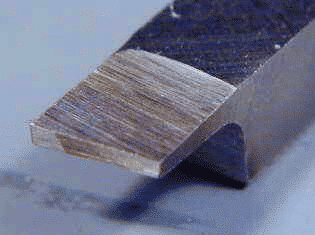
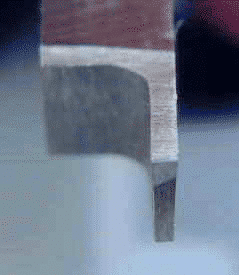
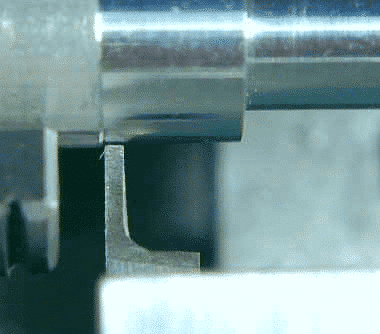
Clamp workpiece
Separation always takes place close to the chuck jaws – no more than 1 / 2 “, preferably no more than 1 / 4”. Parting cutting exerts great tangential force on the workpiece. If the cutting is too far away from the chuck claw, the workpiece may be extruded from the chuck.
Adjust the cutter head
For parting cutting, the top of the tool should be exactly on the center line of the lathe, or no more than 0.005 “of the center line. If the tool is a little higher, it will tend to “climb” the workpiece; if it is a little lower, it will tend to dig in. The tip of the tool should be completely perpendicular to the workpiece.
Speed and Feed
Make sure the leadscrew is in the neutral position so that the leadscrew is not moving. Now lock the half nut in the engaged position to keep the carriage from moving during the parting cut. Parting cuts should be made at low speed; say 200-300 RPM or even slower.
Making the Cut
With the tip of the tool just beyond the surface of the workpiece, turn on the lathe. Slowly advance the cross-slide crank until the tool starts cutting into the metal. Keep advancing the tool until you get a steady chip curling off the workpiece and then try to maintain this cutting speed.
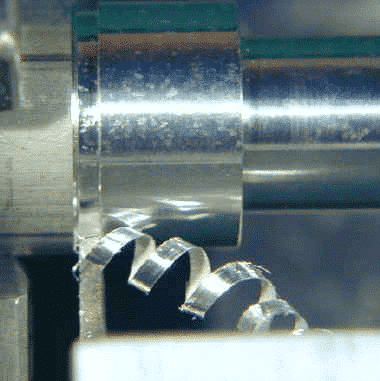
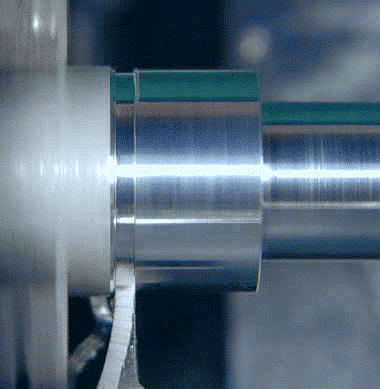
It’s a good idea to use cutting oil for a parting cut and you will find that the heat generated will most likely cause a fair amount of smoke as the cutting oil burns off. Avoid breathing this smoke cause I’m sure it’s not good for your lungs, although no proof says it has bad effect . A small fan to disperse it may be a good addition to your workbench.Chatter
Parting often causes ‘chatter’. If you have never heard this sound, you will easily recognize it when you first do. It is a pulsing, whining vibration that can shake the whole lathe and even cause it to move around on the workbench if is not bolted down. You can stop chatter quickly by backing off the pressure on the tool. The trick is to find the right speed at which to advance the tool with minimal chatter.
Here are some tips to minimize chatter:
- Tool tip should be quite sharp
- Top of tool should be right on the lathe center line
- Tool should be perpendicular to the work piece
- Gibs on cross-slide and compound should be snug
- Saddle should be snug to the ways
- Use carriage lock to lock saddle to ways
- Use cutting fluid
- Maintain steady advance of cross-slide
Finishing the Parting Cut
Keep advancing the tool until it reaches the center of the workpiece. As you get close, the workpiece is suspendend by a thin stalk of metal.
Be careful: if the workpiece extends from the chuck more than a few times its diameter, the end of the workpiece can start to swing in a dangerous arc. As you get near the center, you may need to slow down the chuck speed to keep things safe. If you notice the workpiece starting to wobble, stop the lathe and move the workpiece back and forth by hand to break it free.
The end of the workpiece that you cut off will generally have a pretty rough finish and a little stalk of metal protruding from the end.

One limitation of parting tools is the diameter of the work that can be parted. The tool illustrated here is a little under 3/8″ long and can part off work up to 3/4″ in diameter. In the previous picture you can see that the edge of the work is rounded because it was rubbing up against the shoulder of the cutting tool. If you make the tip of the tool much longer than about 1/2″ it starts to get too limber and will easily break off. So on a small lathe like this, the largest diameter work that you can part off is probably around 1″. To cut off bigger work, you can use a small hacksaw while turning the work at low speed in the lathe. Even better, if you have a metal-cutting bandsaw, use it to cut off the work. I nearly always use the bandsaw for work larger than 1/2″ diameter.
The final step it to mount this piece in the chuck and make a facing cut to clean up the end. One problem with this step is that the chuck jaws can mar the finished workpiece. If you look carefully at the next picture you can actually see the imprint of the chuck jaws. To avoid this, you could wrap the workpiece in a thin strip of emory paper, or similar protective material, before clamping it.