?????
Ordinary wood screws are widely used in the furniture manufacturing industry. Most wood screws are made of Q235A steel and are formed by cold extrusion, offering advantages such as low cost, high efficiency, and large-scale production. Although screws used in the human body are structurally similar to ordinary wood screws, they must possess certain strength and corrosion resistance. Medical screws made from 1Cr18Ni9Ti stainless steel are difficult to produce via cold extrusion on dedicated machines due to material properties, small-batch production, and the need for specialized tools.
Challenges in Machining Medical Screws
For small-batch production of medical screws, CNC machining can be used to compensate for the limitations of dedicated machines. Medical screws have small diameters and relatively large pitches, resulting in poor rigidity. When using forming tools on conventional lathes, the cutting resistance increases as the tool’s cutting depth increases. Due to the small diameter and long length of medical screws, even with supporting methods to counteract most of the cutting resistance, deformation often occurs, making machining difficult. CNC machining offers high efficiency and strong adaptability. Using macro programs for thread turning ensures that the contact area between the tool and the workpiece remains constant, preventing an increase in cutting resistance with deeper cuts. However, medical screws with poor rigidity are still prone to deformation and bending. This paper conducts an in-depth study on the machining of stainless steel medical screws, addressing the challenges of machining stainless steel through reasonable process settings on CNC lathes. By designing supporting fixtures and programming macros for layered turning, the issue of insufficient rigidity in thread processing is resolved.
Principles of CNC Machining for Medical Screws
The key to producing qualified parts lies in the rational planning of the toolpath based on the geometric characteristics of medical screws. CNC machining of threads uses coated carbide inserts. The appropriate spindle speed for turning medical screws must be calculated based on the insert’s allowable cutting speed (v) to ensure reasonable tool life. The formula is:
v=nD/1000
Where:
v is the cutting speed (m/min),
D is the workpiece diameter (mm),
n is the spindle speed (r/min).
In medical screw thread machining, the main cutting force accounts for over 90% of the machine’s total power consumption, while the feed resistance accounts for over 5%. If forming tools are used on CNC machines, the contact area between the tool and the workpiece increases with cutting depth, leading to higher cutting resistance. This can cause vibration, deformation, and bending of the workpiece, making machining impossible.
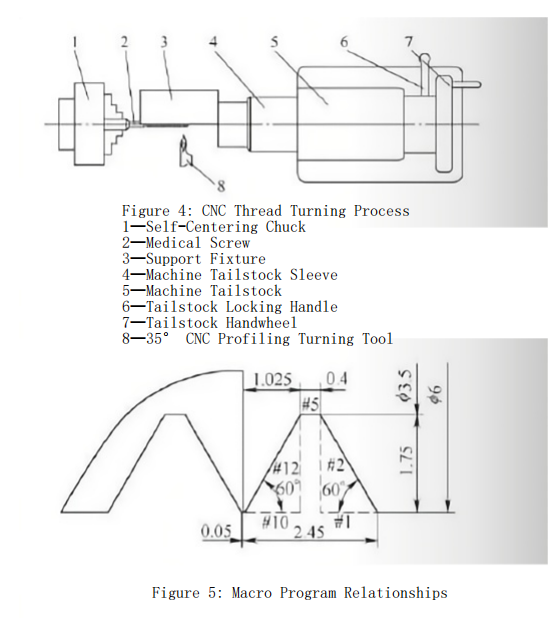
Therefore, traditional forming tools cannot meet the requirements for machining medical screws. To address this, the machining method is improved by using a 35° profiling turning tool. By programming macros to control the toolpath according to the thread profile, the tool completes the profile before performing layered cuts. This ensures that the contact area between the tool and the workpiece remains constant, and the cutting force remains stable and small, overcoming the drawback of increasing cutting resistance with traditional forming tools.
Implementation of CNC Machining for Medical Screws
Selection of Tool Materials
Medical screws are primarily used to connect artificial joints and bones, requiring strength and corrosion resistance. Therefore, 1Cr18Ni9Ti stainless steel, which is acid-resistant, alkali-resistant, and corrosion-resistant, is chosen. This stainless steel has high strength, significant plasticity, and severe hardening during machining, resulting in high cutting resistance and a tendency for deformation. Additionally, the tool is subjected to high cutting temperatures, leading to built-up edge formation.
Due to the tendency of medical screws to undergo work hardening, making machining difficult, tool inserts with low adhesion, high heat resistance, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity should be selected. Adequate cooling during machining is essential, and water-based cutting fluids with good heat dissipation properties are recommended.
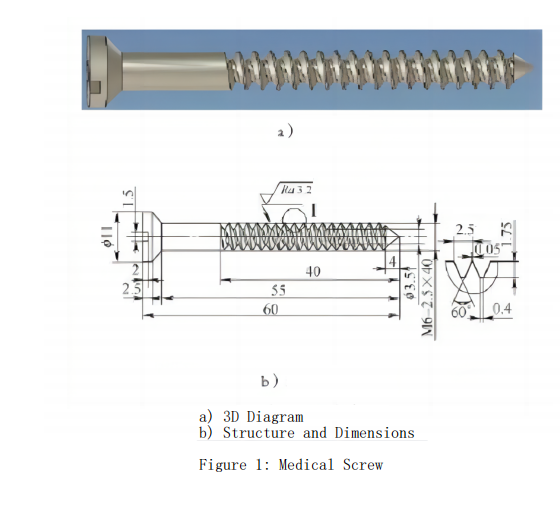
Structure and Dimensions of Medical Screws
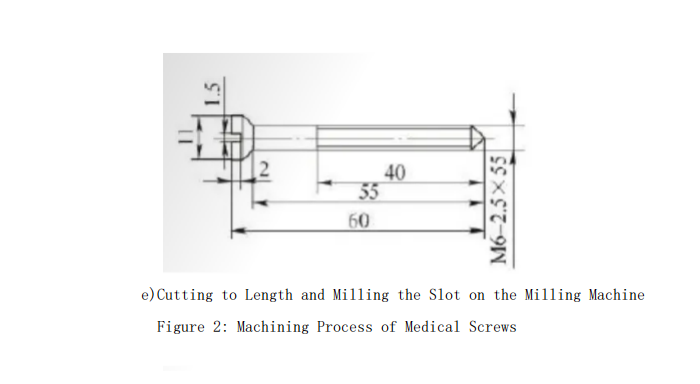
As shown in Figure 1, the medical screw specifications are M6-2.5mm × 55mm, with an outer diameter of 6mm, a pitch of 2.5mm, a root width of 0.4mm, a crest width of 0.05mm, a thread angle of 60°, a length of 55mm, and a maximum diameter of 11mm at the right end. Due to the poor rigidity of the part and the relatively large pitch compared to the diameter, challenges exist in enhancing workpiece clamping rigidity and programming CNC macros.

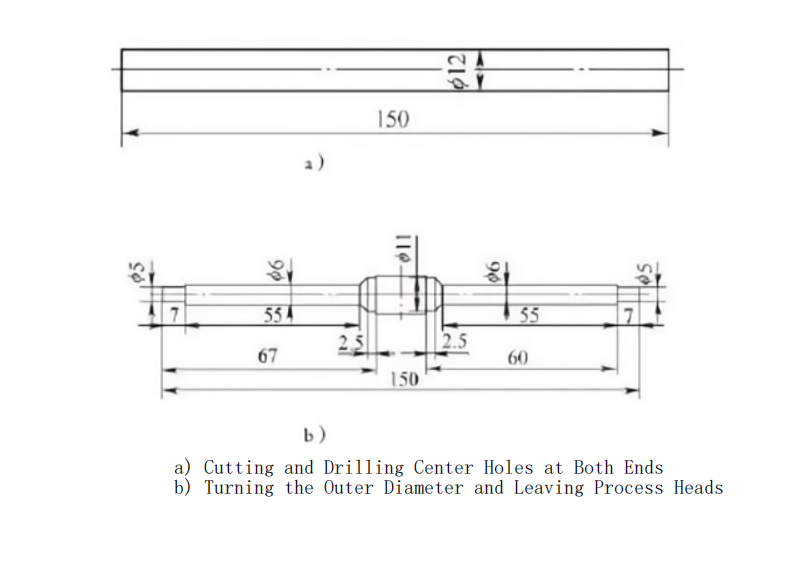
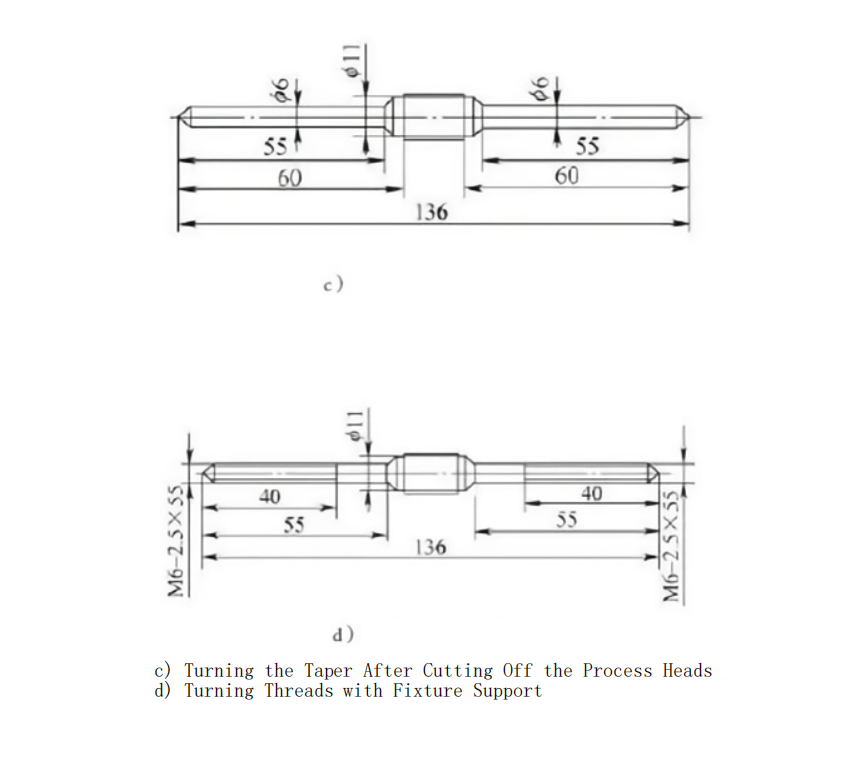
Machining Process
Medical screws are produced in small batches. If a conventional one-clamp-one-center method is used for thread turning, the poor rigidity of the workpiece makes it unable to withstand the cutting forces, leading to bending deformation in the middle. Therefore, the workpiece must be fully supported during thread turning to ensure stability and prevent deformation. A dedicated supporting fixture is designed to assist in supporting the screw.
To reduce cutting resistance and prevent deformation during thread turning, a 35° profiling turning tool with titanium carbide coating is selected. A macro program is written using the trajectory synthesis method for layered thread cutting, significantly reducing cutting resistance and maintaining stability.
The machining process for medical screws is shown in Figure 2. The specific steps are:
Two parts are machined together, with an extra 15mm in the middle for self-centering chuck clamping and 7mm at each end for center drilling.
Turn the 6mm and 11mm outer diameters using a one-clamp-one-center method.
Clamp the 6mm outer diameter and remove the process heads, eliminating the center holes and allowing complete taper turning at both ends.
Clamp the 11mm outer diameter, support the 6mm outer diameter with the fixture, and turn the threads using the macro program.
Cut the two connected screws and trim them to ensure a 60mm length.
Use a horizontal milling machine with a vertical rotary table to clamp the part and mill a 1.5mm wide slot with a saw blade cutter.
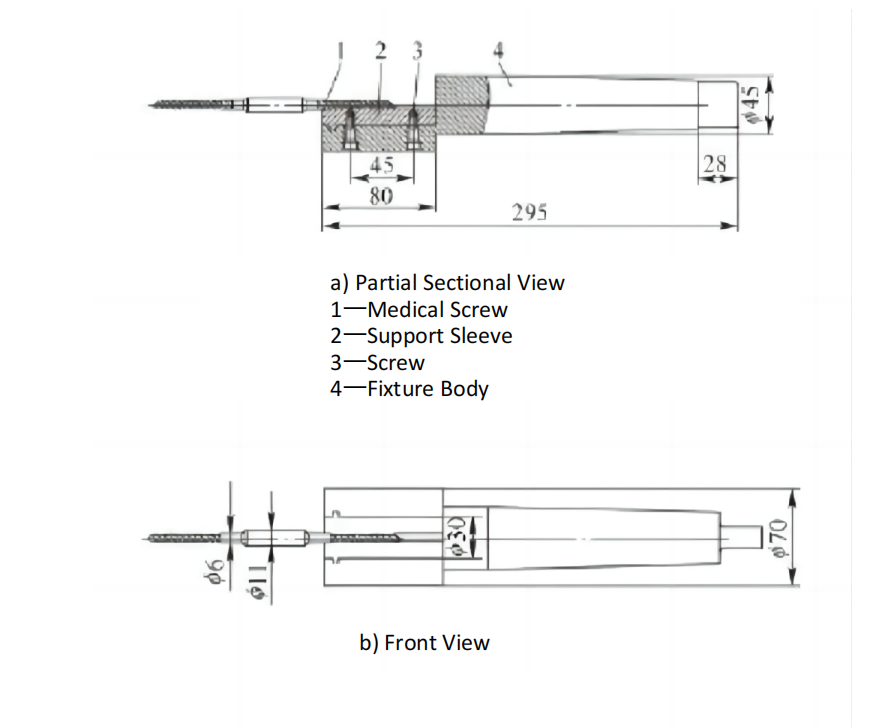
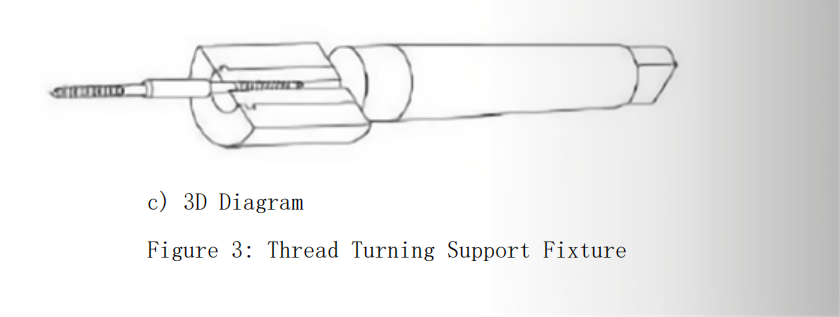
Working Principle of the Thread Turning Support Fixture
As shown in Figure 3, the thread turning support fixture supports the medical screw during machining. Two screws are machined together to facilitate small-batch production. The support sleeve is made of HT200 gray cast iron, which has a low friction coefficient. The protrusion on the support sleeve provides axial positioning, while two screws connect and secure the support sleeve to the fixture body. The left end of the fixture body positions the support sleeve, and the right end has a standard Morse taper No. 5. The fixture is mounted on the CNC lathe’s tailstock, and the tailstock is moved during thread turning to support the screw’s outer diameter, effectively counteracting the cutting resistance. CNC thread turning is shown in Figure 4.
Machining Precautions and Quality Inspection
During the machining of medical screws, the error in the 6mm outer diameter should be controlled within approximately 0.04mm. A larger error would reduce the fit between the 6mm semi-circular hole in the support fixture and the screw’s outer diameter, weakening the fixture’s support and causing vibration or deformation during turning. Additionally, the tool must remain sharp during thread turning, and tool changes should be avoided to prevent thread misalignment.
The 6mm outer diameter of the medical screw is measured with a micrometer, the thread pitch is measured with a caliper, and the surface roughness is checked with a comparator to ensure it meets the Ra 3.2μm requirement. After inspection, the parts fully meet the dimensional requirements and are suitable for use.
????????
Through the analysis of CNC machining principles for medical screws, the design of supporting fixtures, and the programming of macros, the CNC machining of medical screws has been successfully implemented, addressing the shortcomings of cold extrusion for ordinary screws. This method achieves small-batch production of medical screws at a lower cost, providing a reference for machining similar screws made from special materials.