Experimental Content and Method
Test Materials of WC powder
(1) Ultra-fine tungsten powder: The ultra-fine tungsten powder is prepared by the ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method from ultra-fine WO? powder, which is generally amorphous with an average particle size of 25~30 nm. It is reduced by hydrogen at a medium temperature (750~780℃) to obtain tungsten powder with an average particle size of ≤0.35μm (BET particle size).
(2) Carbon black powder: Carbon black powder is produced by two methods: one is by cracking ethane and propane (at 850℃) and then subjected to high-energy ball milling for different periods to produce carbon black powders with average particle sizes of 0.1 and 0.3 μm, respectively; the other is from activated carbon powder with an original particle size of 100~200μm, which is subjected to high-energy ball milling for different periods to produce carbon black powders with average particle sizes of 0.8 and 4.5 μm, respectively.
Experimental Method
Using ultra-fine tungsten powder with the same particle size (0.35 μm) and four different particle sizes (0.1, 0.3, 0.8, 4.5 μm) of carbon black powder, the carbon is blended according to the reaction formula W+C=WC (with an additional loss of 0.1%). The mixture is ball milled for 1.5 hours in a conventional ball mill with a ball-to-material ratio of 1:1. The heat-resistant stainless steel boat containing the mixed material is placed in a stainless steel tube furnace and carbonized under a hydrogen atmosphere. The holding time is 40 minutes for all. In the temperature range of 830~1300℃, the carbonized material is taken out at different temperatures, cooled, and then removed from the furnace. Subsequently, XRD phase analysis and chemical analysis are conducted to determine the total carbon and free carbon, and the amount of combined carbon in WC is calculated. Finally, the quantitative relationship between the particle size of carbon black powder and the phase composition and combined carbon content of WC powder under different carbonization temperatures can be plotted.
Test Results and Discussion
Figure 1 shows the effect of carbon black powder with different particle sizes carbonized at different temperatures on the combined carbon content of WC powder. Curve 1 in Figure 1 represents the relationship between carbonization temperature and the combined carbon content of WC powder when using ultra-fine carbon black powder with a particle size of 0.1 μm. As can be seen from Figure 1, when using 0.1 μm ultra-fine carbon black, the combined carbon content of WC powder can reach 5.8% (by mass), which is equivalent to 95% of the theoretical content, at a very low carbonization temperature (850℃). When the temperature is greater than 950℃, the carbon content of WC powder can reach the theoretical content. This result indicates that the carbonization reaction can be completed at a low temperature when using ultra-fine tungsten powder in conjunction with ultra-fine carbon black powder. This phenomenon suggests that the ultra-fine W powder particles are carbonized before they undergo significant aggregation and growth.
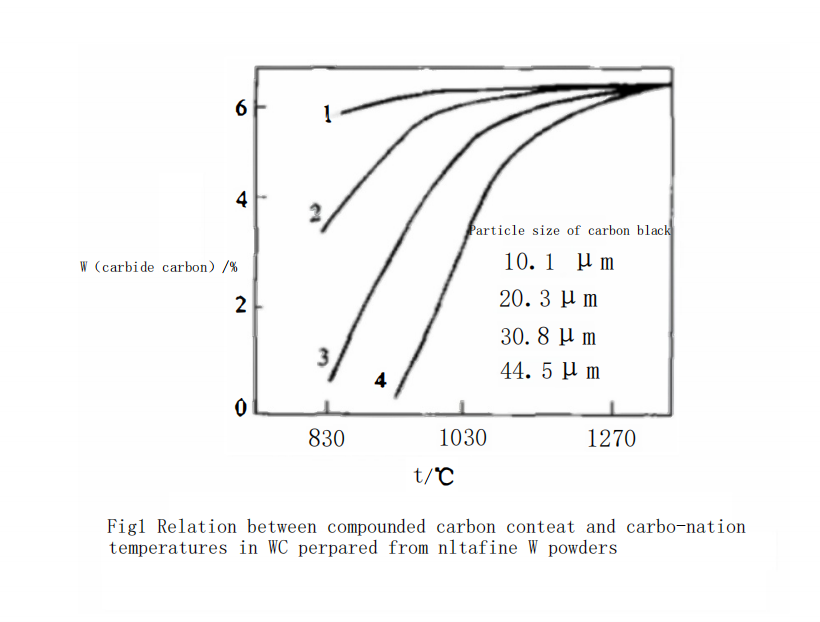
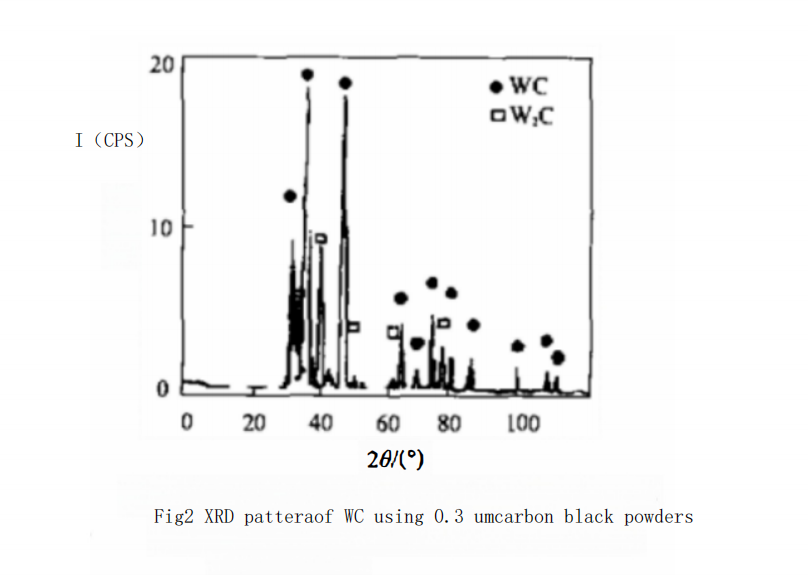
At this temperature, as the particle size of the carbon black used increases, the combined carbon content in WC powder rapidly decreases. For example, as shown in Curve 2 of Figure 1, when using 0.3 μm carbon black at 950℃ with the same holding time of 40 minutes, the combined carbon content of WC powder only reaches 5.2% (by mass). XRD analysis indicates that there is still significant W?C in the WC powder, as shown in Figure 2. The free carbon phase was not detected due to its low content. The combined carbon content in WC powder can only reach the theoretical value when the temperature is increased to 1060℃. Its complete carbonization temperature is about 130℃ higher than that of the 0.1 μm carbon black.
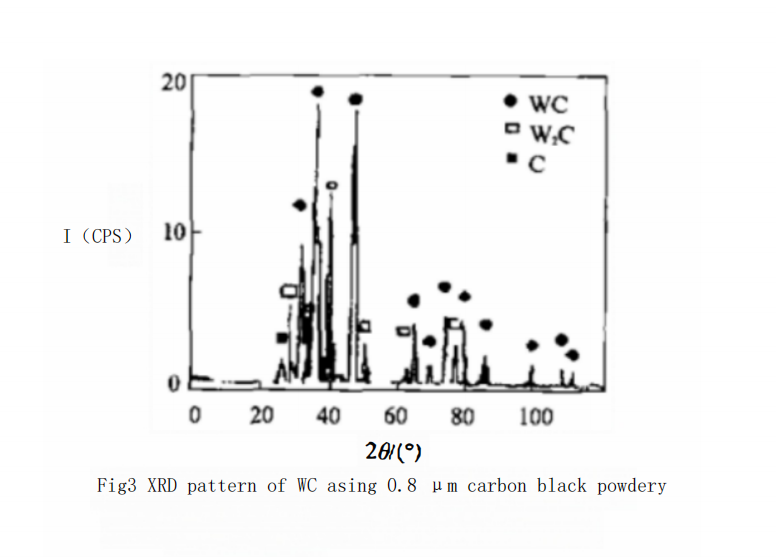
When using 0.8 μm carbon black, as shown in Curve 3 of Figure 1, at 950℃ with a holding time of 40 minutes, the combined carbon content of WC is only 3.18% (by mass). XRD analysis indicates that in addition to the obvious W?C phase, there is also significant free carbon present in the WC powder, as shown in Figure 3. The combined carbon content in WC powder can only reach the theoretical value when the carbonization temperature is increased to 1230℃. The temperature required for complete carbonization has increased significantly.
The reason for this phenomenon is that when the carbon content ratio is constant, the finer the carbon black particle size, the easier it is to mix uniformly with W powder particles, increasing the contact area between them. Undoubtedly, fine-grained carbon black will accelerate the carbonization rate. Moreover, the finer the carbon black particle size, the more its specific surface area and the number of active carbon atoms on the surface increase dramatically. Thus, the carbonization reaction rate between carbon and tungsten accelerates, and the complete carbonization temperature decreases with the decrease of carbon black particle size.
Conclusions
(1) When the particle size of ultra-fine W powder is the same (≤0.35μm), the combined carbon content in WC powder decreases significantly with the increase of the carbon black particle size at a certain temperature.
(2) When the particle size of carbon black is constant, the content of combined carbon increases with the rise of carbonization temperature.