
production of screw
Processing of wire
Fastener screws are typically made from wire materials with diameters ranging from 5 to 19 mm. The main materials used for these screws include carbon steel, stainless steel, and copper.
Rough machining of wire
To remove the oxidation layer that forms on the wire material during production and storage, a coarse drawing process is necessary. After this treatment, the wire surface will exhibit its original metallic luster.

The coarse drawing process consists of two steps:
1.Annealing: This step involves adjusting the crystalline structure, reducing the wire’s hardness, eliminating graininess, and improving the wire’s machinability at room temperature.
2.Acid pickling and phosphating: A layer of phosphate salt film is formed on the metal surface. This step makes the wire more suitable for further shaping and reduces wear and tear on the molds during subsequent processes such as wire drawing and cold forging.
3.finishing process of wire
This step involves drawing the wire to the desired wire diameter thickness based on the specific product requirements and specifications. This is done to facilitate further processing and shaping.
4.Final molding process
This step is divided into three stages:
Cold Heading: Using a cold heading machine to cut the wire into the desired length, create screw heads, and add markings.
End Trimming: Shaping the wire into a dovetail shape for penetration through steel plates.
Threading: Adding threads to the semi-finished product.
5.Hot pressing
Cleaning: Removing grease from the surface of the screw.
High-temperature carburizing: Allowing carbon atoms to penetrate the surface layer of the screw, increasing its hardness.
Quenching: Forming a crystal layer on the surface of the screw to achieve the final hardness requirements.
Cleaning quenching oil: Removing quenching oil from the surface of the screw.
Low-temperature tempering: Reducing the core hardness of the screw to make it more ductile and prevent breakage due to excessive core hardness.
6.Electroplating
The purpose of electroplating is to prevent screws from rusting, extend their lifespan, and improve their appearance. Galvanizing, chromium plating, nickel plating, and copper plating can mitigate corrosion on the screw’s surface.

Brief intro of cold heading
In fact, the manufacturing methods of screws can be divided into cold heading, hot forging, and machining (turning, milling, etc.). Cold heading involves using the metal’s plasticity and applying pressure or cold drawing at room temperature to achieve solid-state deformation of the metal. It is a method for shaping the top of a bar or wire by increasing its thickness.
Applications of cold heading: It is mainly used for manufacturing parts such as bolts, nuts, iron nails, rivets, and steel balls. Forging materials can include copper, aluminum, carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and titanium alloys, among others.
Advantages of cold heading: Material utilization can reach 80-90%, and it offers high production efficiency, often exceeding 300 pieces per minute.

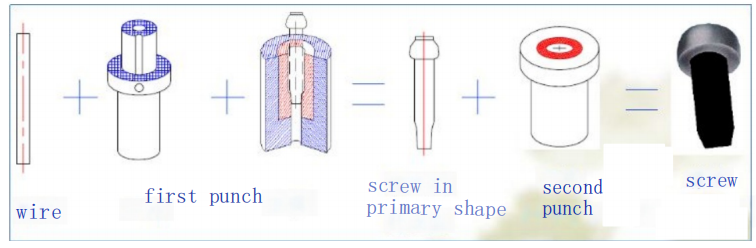
Procedures of cold heading
Through the interaction between the molds, the wire is cut and upsetting to form a screw blank, forming the head, cross slot (or other head shape), thread blank diameter and rod length, and head fillet.
Selection of material of cold heading molds
During cold heading, the metal blank undergoes plastic deformation due to impact pressure at room temperature, causing a redistribution and transfer of the blank’s volume within the die to achieve the desired shape. Cold heading forming processes are primarily used for the production of fasteners (various types of screws and nuts). Cold heading dies have to withstand high impact forces per unit pressure, which can reach 2000-2500 MPa, and the impact frequency is very high. The die’s cavity surface and the working surface of the punch also experience strong impact friction, and the working temperature can reach around 300°C. The punch also undergoes bending tension.
The choice of steel materials for cold heading dies should be based on factors such as the working conditions of different parts of the die, cross-sectional size, depth of the hardened layer required, and production batch size due to the characteristics of the working conditions of the cold heading dies and the shallow depth of the hardening layer.
1.For lightly loaded small concave dies, it is common to use integral modules with a surface that has a certain hardened layer. When a shallow hardened layer depth is required, materials like T10A steel can be used. If a deeper hardened layer is needed, low-alloy tool steels may be chosen. High-carbon chromium steel, or high-speed steel, or composite materials are not suitable in such cases.
2.For heavily loaded and complex-shaped concave dies, high-carbon medium chromium steel, high-speed steel, or a base steel embedded module may be chosen. These insert modules can be embedded using press-fit or hot-insert methods into a mold liner made of a material with good toughness.
3.When the production quantity exceeds 200,000 pieces, cemented carbide or steel-bonded cemented carbide insert modules may be considered. These materials offer high wear resistance, tight tolerances, and long service life, which can compensate for their higher cost. They are used for cold heading punches and should have good anti-friction and wear resistance properties. Additionally, they should possess sufficient hardness to prevent collapse in areas exposed to impact.
4.For low loads, T10A steel or low-alloy tool steel is often used. For larger mold dimensions and heavy loads, modular assembled die sets using the same material as the concave die are recommended.








