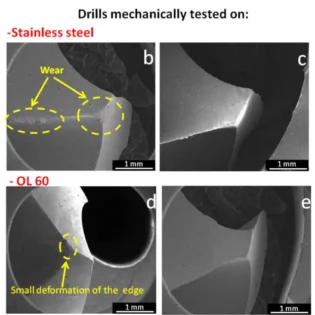
Figure 1: Simplified model of chip formation
During the machining process, the material removed undergoes plastic ?deformation and shearing within the shear plane and is expelled in long or short chip forms depending on the properties of the workpiece material. A significant amount of energy is consumed in the shear zone of the machining process. For machining incompressible materials, the deformation of material within the shear plane does not change its volume. Assuming deformation is simple shear and placing a stack of material layers parallel to the shear plane, chip formation can be viewed as a shearing process of these material layers.
Material Properties and Chip Formation
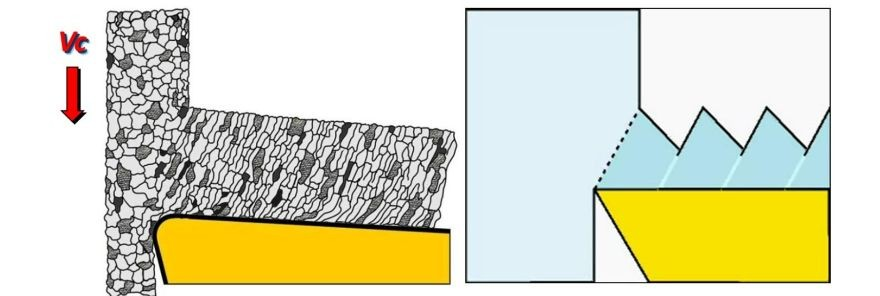
Numerous factors influence chip formation, particularly the properties of the workpiece material. Metal cutting processes involve plastic deformation of the workpiece material followed by shearing. Elastic and plastic material behaviors play a decisive role in this process. Different workpiece materials exhibit varying combinations of shear strength and ductility. Ductility of the workpiece material refers to the extent to which it can be deformed before fracturing (see Figure 2). The higher the ductility of the workpiece material, the longer the chips. As a rule of thumb, when the ductility of the material exceeds approximately 25%, chips range from long to very long.
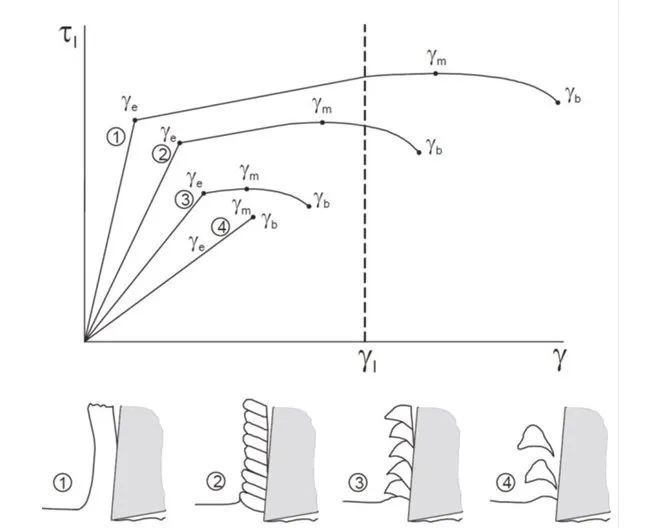
Figure 2: Influence of plastic and elastic properties of workpiece material on chip formation.
Some workpiece materials produce long chips; some produce long and ductile chips, while others produce short chips. This method is also used in the ISO system for classifying different types of workpiece materials. Since each ISO group (P, M, K, N, S, and H) produces predictable chips, the selection of tools and cutting conditions must match the material behavior. ISO Group P (steel) comprises materials with relatively high ductility and a tendency to form long chips. Proper precautions need to be taken to maintain the acceptable form and length of chips.
ISO Groups K (cast materials) and H (hardened steels) include materials with lower ductility that produce short chips. This simplifies chip control. ISO Groups M (stainless steel), S (super alloys), and N (non-ferrous materials) include materials with relatively low ductility but noticeably viscous. These materials form so-called “Built-up edge” chips.
Figure 3: Classification of chip morphology and shapes.
Classification of Chip Morphology and Shapes
Chips can be classified from very long to very short, with ideal chips avoiding any extremes. Chips that are too short can make machining intermittent, leading to premature tool edge chipping and shortened tool life. From the perspective of tool life, longer chips are preferable. Long and smoothly shaped chips result in fewer micro-vibrations during the machining process, leading to better surface quality. However, from the perspective of the cutting process itself, long chips are not ideal. They can damage the machine, workpiece, and tools, creating unsafe conditions for operators. They can also pose ejection problems in chip conveyors, increasing production downtime.

Figure 4: Classification of chips, from long to short. From left to right: Ribbon, Tangled, Helical, Long Helical, Helix, Ideal Helix, Helical Pipe, Long comma, and Short comma chips.
Short chips eliminate ejection problems but indicate intermittent cutting, which may lead to shorter tool life (due to tool edge chipping) and micro-vibrations that degrade surface quality. Helical-shaped chips are neither too long nor too short, representing an ideal state, providing the best opportunity for optimal cutting operations.
Ideal chip formation, Short Helical type

Low power requirement
Low stress on cutting edges
Low cutting force Easier to eject
Avoid very short chips

High power requirement
High stress on cutting edges
May cause tool or workpiece deflection and vibration
Avoid long and ribbon-shaped chips
Difficult to eject
Dangerous for operators
May re-cut and damage the workpiece or tool